Introduction
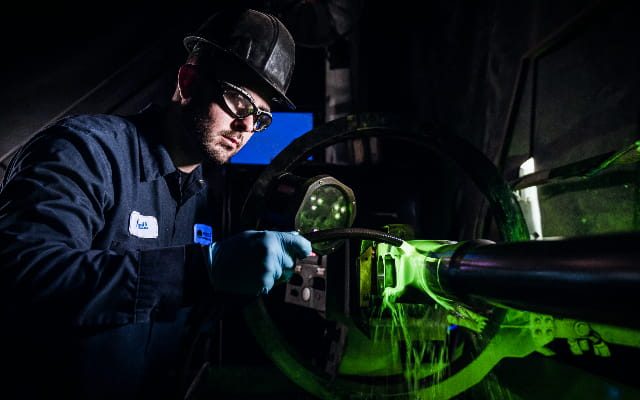
Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT) is a famous non-destructive testing method to see the cover and barely subterranean discontinuities in ferromagnetic fabrics is Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT). For this technique to operate, a magnetic field must first be created within the test item before iron oxide or iron oxide-coated particles are applied to the surface.
The particles will be drawn to and gathered at any surface-breaking, near-surface crack, or discontinuity, creating a visual signal. MPT is employed in several sectors, including manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and construction, to examine crucial parts for flaws that might result in catastrophic failures. We will talk about efficient ways to test magnetic particles in this post.
Magnetic particle testing techniques:
Direct Current (DC) Yoke Method:
This technique encircles the test object with a yoke or a horseshoe-shaped magnet. Iron oxide or iron oxide-coated particles are then put to the item’s surface after the yoke creates a magnetic field within it. The particles will gather around any surface-breaking or near-surface discontinuities, creating a clear indicator.
The intensity of the magnetic field, the particle concentration, and the size and form of the defect all affect how well this procedure works. This technique is excellent for checking huge and intricate objects like welds, pipelines, and plates. However, it could be more effective for identifying minute and substantial flaws.
Alternating Current (AC) Yoke Method:
Like the DC yoke method, the AC yoke method uses alternating rather than direct current. Compared to the DC yoke approach, the alternating current method generates an oscillating magnetic field that may identify more minor and deeper flaws.
This technique frequently checks castings, forgings, and thin sheets. In contrast to the DC yoke approach, visual indicators need a greater particle concentration.
Approach Using Prods or Coils:
In this technique, Magnetic Particle testing is created inside the item using a hand-held probe or a coil. The object’s surface is then covered with iron Oxide or iron oxide-coated particles, and any surface-breaking or near-surface discontinuities will cause the particles to cluster around the defect, creating a visual indicator.
This technique perfectly checks complex and tiny objects like gears, shafts, and bearings. To keep the probe in constant touch with the item’s surface, though, a trained operator is needed.
Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL) Method:
More sophisticated technology is used to check pipes and tanks for corrosion and other flaws: the MFL method. This technique sends a magnetic field through the object’s wall and magnetizes the substance.
It is possible to utilize sensors to find any discontinuity or corrosion on the wall causing the magnetic flux to seep out of the material. This technique can swiftly check lengthy pipe lengths and is very successful at finding concealed corrosion. However, it needs specialized gear and skilled operators.
Dry Powder process:
This technique puts iron oxide or iron oxide-coated particles on the object’s surface. Any surface-breaking or near-surface discontinuities will cause the particles to collect around the defect, creating a clear signal.
Forgings and castings with rough and uneven surfaces respond well to this inspection. However, because the particles might not stick to the surface, checking polished or flat surfaces is inappropriate. This procedure can be messy if not well confined and needs a high particle concentration to create noticeable results.
Conclusion
The convenient and well-liked non-destructive technique known as Magnetic Particle testing may detect surface and marginally subsurface discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials. The process includes coating the test object with iron oxide or iron oxide-coated particles while also inducing a magnetic field inside the object.
Any fracture or discontinuity that breaks the surface or is close to it will attract the particles, which will then collect there and provide a visible signal. How efficient the process is will depend on the methods and equipment used.
Depending on the object’s dimensions, form, material composition, and the type of imperfection being looked out for, a particular strategy will be taken. The prods or coils method, the AC yoke method, and the DC yoke method are the three ways that make up the five discussed in this article.
Read More: Discovering the Benefits of Non Destructive Testing Companies