Sand casting stands as a time-honored method in the realm of metal casting, offering a versatile and cost-effective approach for producing intricate metal components. Within the intricate web of sand casting techniques, the role of cores emerges as a pivotal factor, unlocking the full potential of this age-old method. This article delves into the realm of sand casting, shedding light on the significance of cores and their role in enhancing the versatility of the entire casting process.
Understanding Sand Casting:
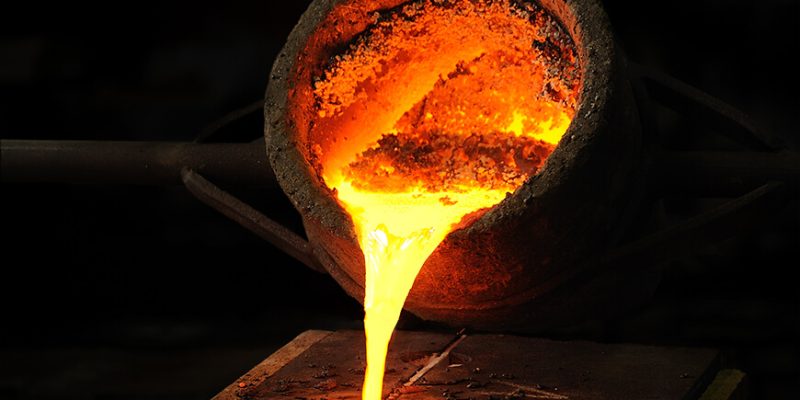
Before delving into the versatility boost provided by cores, it is essential to comprehend the fundamentals of sand casting. Sand casting, one of the oldest known metalcasting processes, involves creating a mold made of sand to form a cavity into which molten metal is poured. Once the metal solidifies, the casting is removed from the mold, revealing the desired product. Sand casting is renowned for its adaptability, allowing the production of a wide array of complex shapes and sizes.
The Role of Cores in Sand Casting:
Cores in sand casting act as internal molds within the main mold, forming the internal cavities of the casting. These cores are typically made of sand or a similar material and are strategically placed within the mold to create voids or passages in the final product. The versatility of sand casting is significantly augmented by the use of cores, as they enable the production of complex and intricate components that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with a single-piece mold.
Versatility Boost:
- Intricate Geometries:
Cores in sand casting empower manufacturers to craft intricate geometries that go beyond the limitations of a single-piece mold. The ability to create hollow or complex internal structures within a casting opens up new possibilities for designers and engineers, allowing the production of components with sophisticated shapes and functionalities.
- Reduced Material Usage:
Cores contribute to the efficient use of materials in sand casting. By using cores strategically, manufacturers can reduce the amount of metal required for a casting, resulting in cost savings and a more sustainable casting process. This reduction in material usage also makes sand casting an attractive option for projects with budget constraints.
- Enhanced Cooling and Solidification Control:
Cores play a crucial role in controlling the cooling and solidification of the molten metal. By strategically placing cores within the mold, manufacturers can influence the rate at which different sections of the casting solidify. This control over solidification helps prevent defects such as shrinkage and porosity, contributing to the overall quality of the final product.
- Multi-Material Castings:
The use of cores enables the creation of multi-material castings in sand casting. By incorporating different cores for distinct sections of the casting, manufacturers can produce components with varying material properties within a single product. This versatility is particularly beneficial in applications where different sections of a component require specific mechanical or thermal characteristics.
- Improved Design Flexibility:
Cores provide designers with increased flexibility in creating intricate and complex designs. The ability to incorporate internal structures and features enhances the design possibilities, allowing for the production of components that meet specific performance requirements. Sand casting with cores becomes a go-to method for industries demanding both complexity and adaptability in their metal components.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the versatility boost provided by cores in sand casting is a testament to the adaptability and innovation inherent in this age-old metalcasting technique. From intricate geometries to improved material efficiency, cores play a pivotal role in expanding the capabilities of sand casting, making it a preferred choice for a wide range of applications.
As technology continues to advance, the synergy between sand casting and cores is likely to unlock even greater potential, paving the way for the creation of complex and high-performance metal components across various industries.